方法(Method)
前面有提到物件和類別的關係及屬性,但只有屬性,物件並不會有動作,因此要在類別中用方法來描述物件的行為。
傳回值型別 方法名稱(參數型別 參數名稱…){
敘述1
…
敘述n
}
方法名稱就像取變數名稱的目的一樣,表示類別可進行的動作,讓人快速理解是什麼動作。
()小括號傳入必要的參數,可以留空
{}大括號用來敘述所要執行的動作
無參數的方法
方法在遇到return或整個跑完後,會再跳回呼叫的原處繼續執行。
package com.mycompany.testthree;
class Car{
int tire;
int seat;
void run(){
System.out.println("前進5公里");
}
}
public class testThree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car bus = new Car();
Car auto = new Car();
bus.tire=6;
bus.seat=20;
auto.tire=4;
auto.seat=4;
System.out.print("公車有"+bus.tire+"個輪胎、"+bus.seat+"座位,");
bus.run();
System.out.print("汽車有"+auto.tire+"個輪胎、"+auto.seat+"座位,");
auto.run();
}
}
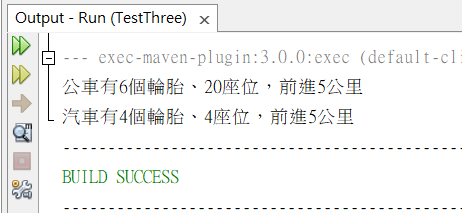
呼叫方法run,讓公車和汽車的行為為前進5公里。
有參數的方法
在主程式指定公車和汽車前進的公里數,作為參數傳進run裡。
package com.mycompany.testthree;
class Car{
int tire;
int seat;
void run(int km){
System.out.println("前進"+km+"公里");
}
}
public class testThree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car bus = new Car();
Car auto = new Car();
bus.tire=6;
bus.seat=20;
auto.tire=4;
auto.seat=4;
System.out.print("公車有"+bus.tire+"個輪胎、"+bus.seat+"座位,");
bus.run(25);
System.out.print("汽車有"+auto.tire+"個輪胎、"+auto.seat+"座位,");
auto.run(10);
}
}
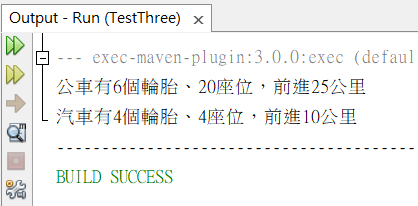
定義同名方法
在Java中,允許在同個類別中,定義同名、但參數個數或型別不同的方法,稱為多重定義(Overloading)。
package com.mycompany.testthree;
class Car{
int tire;
int seat;
void run(int km){
System.out.println("前進"+km+"公里");
}
void run(int start, int end){
int km;
km=end-start;
System.out.println("前進"+km+"公里");
}
}
public class testThree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car bus = new Car();
bus.tire=6;
bus.seat=20;
System.out.print("公車有"+bus.tire+"個輪胎、"+bus.seat+"座位,");
bus.run(25);
System.out.print("公車有"+bus.tire+"個輪胎、"+bus.seat+"座位,");
bus.run(20,100);
}
}
這邊有兩個run方法:
一個是行走公里,一個是開始與結束的一維座標軸位置,同名、但參數個數不同的多重定義。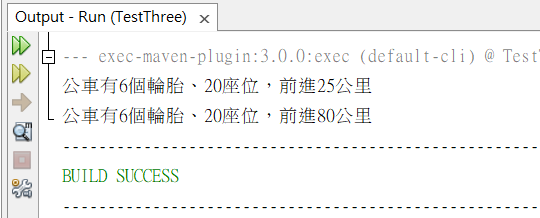
參考資料:
最新java程式語言第六版
